Additive manufacturing is creating an object by adding layer upon layer of material. Additive manufacturing is frequently conflated with 3D printing, but 3D printing is a type of additive manufacturing. There are several other additive manufacturing techniques, including screen printing, sheet lamination, material jetting, and more. Additive manufacturing has been used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, and even food!
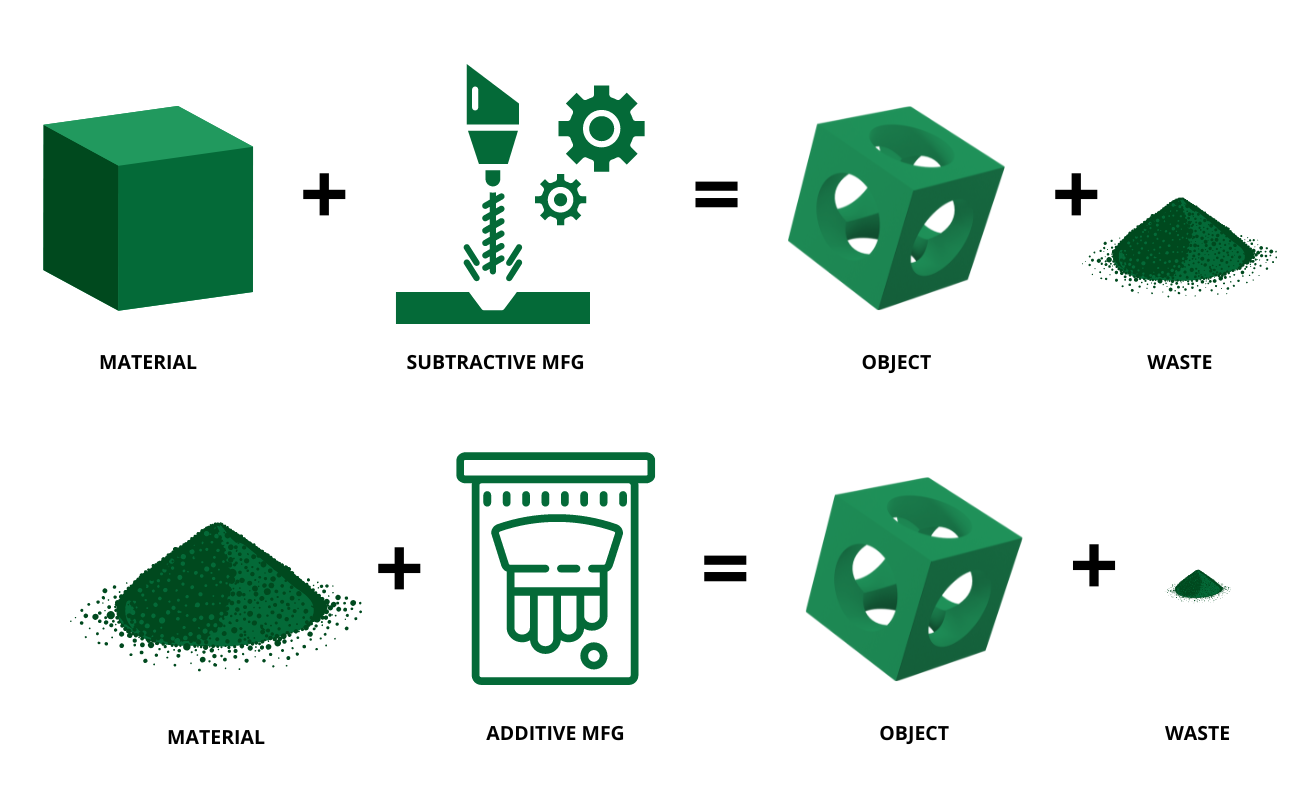
Additive manufacturing has gained attention for being a more sustainable option when compared to its counterpart, subtractive manufacturing. Subtractive manufacturing removes materials to create a finished product. Compared to subtractive manufacturing, including CNC machining and milling, additive manufacturing is more efficient and produces less waste.
As we collectively work towards a greener tomorrow, additive manufacturing can not only help save money but also save the planet. Here are five reasons why additive manufacturing is a sustainable option:
-
Material efficiency
One of the main advantages of additive manufacturing is material efficiency. Traditional manufacturing methods involve subtractive processes, where material is removed from a larger block to create the desired shape. This results in a significant amount of wasted material. In contrast, additive manufacturing builds objects layer by layer, using only the amount of material needed. This means that additive manufacturing can significantly reduce material waste and save resources.
Typical materials used when manufacturing printed electronics, such as biometric sensors and flexible heaters, are conductive inks and flexible substrates. These advanced printed technologies are made with screen printing techniques, a form of additive manufacturing, by layering inks on top of flexible substrates. They are then heat adhered to a garment or finished good.
-
Energy efficiency
Additive manufacturing is also more energy-efficient than traditional manufacturing methods. In subtractive manufacturing, energy is needed to remove material, which can be a time-consuming and expensive process. In contrast, additive manufacturing only uses energy to create the object layer by layer. Additive manufacturing can also operate on a smaller scale, making it perfect for small-batch jobs. With small-batch quantities, less energy is used and only the amount of goods that are required are produced.
We custom make all our products at Butler Technologies, which helps save energy. This means we only produce what our customers request with little extra parts produced. Instead of trashing the additional parts, we recycle and reuse them as samples to provide prospective customers.
-
Local production
Additive manufacturing can enable local production, which reduces transportation and distribution costs. Traditional manufacturing often requires shipping products long distances, which can result in high transportation and logistics costs, as well as environmental impacts. With additive manufacturing, products can be produced on-site or closer to the end user, reducing the need for transportation and logistics.
At Butler Technologies, we produce the majority of our components in downtown Butler, PA. Sometimes, we’ll even hand deliver parts to our customers to cut down on transportation emissions and costs.
-
Design flexibility
Additive manufacturing also allows for greater design flexibility, which can result in more sustainable products. Traditional manufacturing often limits design options due to the constraints of machines or available technology. On the other hand, additive manufacturing enables the production of more complex designs, which can lead to more efficient, lightweight products and require less material.
Advanced printed technology, such as flexible heaters, can be made in various sizes and shapes to fit the customer’s exact space constraints. Customers are not contained by off-the-shelf parts but rather save materials, time, and energy by having a design custom-made to their requirements.
-
Sustainable materials
Finally, additive manufacturing can also use sustainable materials like conductive inks made through cavitation. Conductive inks are made in a closed system, meaning no outgasses or pollutants escape. Subtractive manufacturing often relies on environmentally harmful or difficult-to-recycle materials, such as plastic.
Conductive inks can also be recycled. These inks are typically made from silver because of its highly conductive properties. The silver in ink can be reclaimed and used again, creating a circular economy. At Butler Technologies, we recycled over 14 pounds of silver ink last year and plan to continue to reclaim our expired inks.
While there are still challenges to overcome, such as the availability and cost of sustainable materials, additive manufacturing has the potential to significantly reduce the environmental impact of manufacturers across several industries. If you’re interested in learning if your project is eligible for additive manufacturing techniques like screen printing, reach out to our team today.
